Hearing loss is a decrease in hearing capacity that can affect quality of life. Unlike other hearing disorders, it involves significant hearing loss, which can range from mild to severe. It is important to understand the causes, available treatments, and how we can manage this condition.
Causes of hearing loss
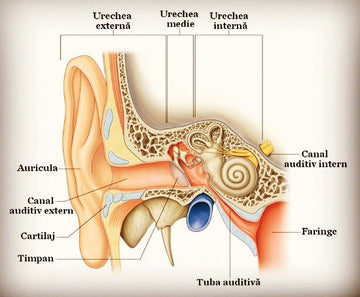
The ear, which is structured into three parts – the outer, middle and inner ear, plays a vital role in the hearing process. Any damage to these parts can lead to hearing loss.
- The external ear
- It collects sound waves and directs them to the eardrum.
- Obstructions such as wax plugs or foreign bodies can hinder the hearing process.
- Middle ear
- It contains the ossicles (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that transmit vibrations to the inner ear.
- Infections or trauma can affect the functioning of this area.
- Inner ear
- It includes the cochlea, which contains sensory cells responsible for transmitting sound signals to the brain.
- The cells in the cochlea do not regenerate, which makes their damage irreversible.
Types of hearing loss
- Unilateral hearing loss: Affects only one ear.
- Bilateral hearing loss: Affects both ears.
Factors contributing to hearing loss
- Genetics: Inherited predispositions may play an important role.
- Acoustic trauma: Exposure to loud noises, such as explosions or concerts.
- Aging: The natural aging process affects sensory cells.
- Infections: Otitis media or other infections can cause temporary or permanent damage.
- Injuries: Head or ear trauma.
- Ototoxic medications: Some medications can damage hearing.
How can hearing loss be improved?
- Medical treatments:
- Infections and inflammations are treated with antibiotics or anti-inflammatories, only on the recommendation of a doctor.
- In the case of acoustic trauma, auditory rest can help.
- Hearing aids:
- Effective solutions for irreversible hearing loss. Hearing aids are available in several models, tailored to individual needs.
- The audiologist will recommend the right model based on an audiogram.
- Cochlear implants:
- Indicated for severe cases of hearing loss, where hearing aids are not sufficient.
- Auditory rehabilitation:
- It includes adaptive therapies and exercises to improve communication.
The impact of hearing loss on life
- Social isolation: Communication becomes difficult, which can lead to avoidance of social interactions.
- Loss of independence: Routine activities, such as using the phone, become complicated.
- Safety risks: Not hearing alarms or sirens can be life-threatening.
- Emotional problems: Stress and anxiety are common among people with hearing loss.
What do you need to do?
- Consult a specialist:
- If you suspect hearing loss, schedule an evaluation with an audiologist or ENT doctor.
- Act quickly:
- Sudden hearing loss requires emergency treatment within the first 72 hours to increase the chances of recovery.
- Avoid self-medication:
- Medications taken without the recommendation of a specialist can worsen the problem.
Conclusion
Hearing loss is a condition that requires attention and early intervention. Although some forms are irreversible, modern treatments and hearing aids can greatly improve your quality of life. If you are experiencing hearing difficulties, don't ignore the symptoms – early diagnosis can make all the difference.